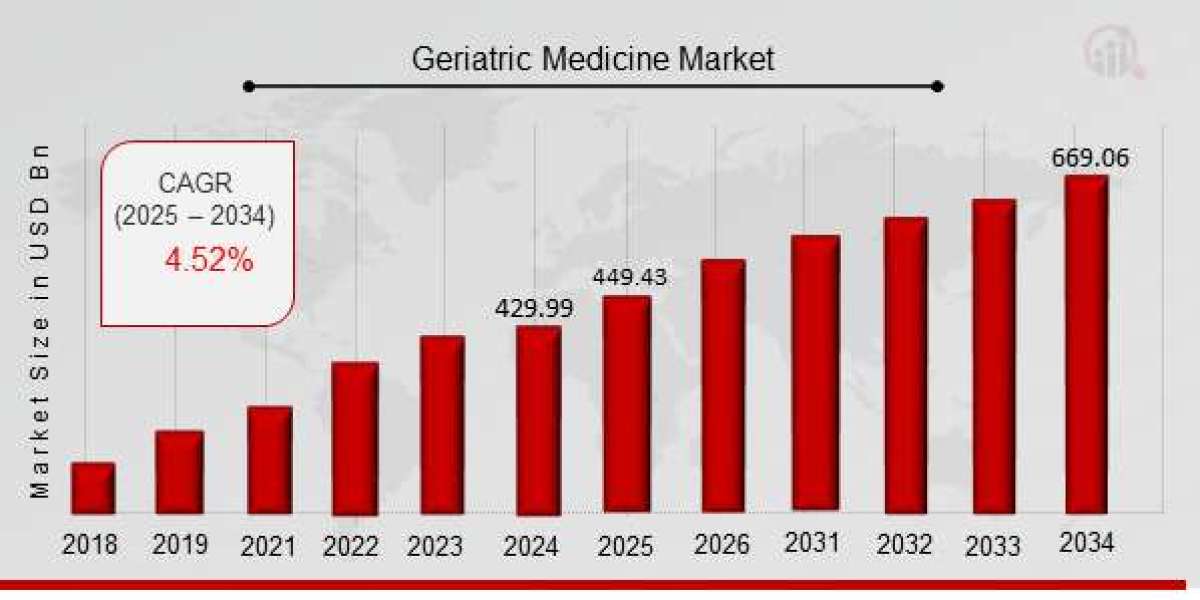
The Future of Geriatric Medicine in 2025: Key Trends You Need to Know
As we move further into 2025, the field of geriatric medicine is evolving rapidly in response to the growing number of elderly individuals worldwide. By 2030, it’s expected that one in every six people on the planet will be aged 60 years or older, which underscores the increasing need for specialized healthcare designed to meet the unique needs of aging populations. In this context, geriatric medicine is not only advancing to address the physiological changes that come with aging but also adapting to the technological, societal, and cultural shifts of the modern world. In this blog, we’ll explore the key trends shaping geriatric medicine and what to expect in the coming years.
1. Aging Populations Driving Demand for Geriatric Care
The most obvious trend driving changes in geriatric medicine is the rapid increase in the aging population. According to the World Health Organization, the global population of individuals aged 60 years and older is growing faster than any other age group. By 2025, it’s estimated that nearly 2 billion people will be over 60, placing enormous pressure on healthcare systems to provide adequate care for the elderly.
This demographic shift is influencing the development of geriatric medicine in a way that focuses on addressing chronic conditions, cognitive decline, and multimorbidity, where individuals suffer from two or more diseases at once. The elderly often present with multiple health conditions simultaneously, and managing these complex cases requires a highly specialized approach. The increasing demand for geriatric care is, therefore, prompting healthcare providers to adjust their services to cater to this growing need, from hospital care to home healthcare services.
2. Technological Advancements in Geriatric Care
One of the most transformative trends in geriatric medicine is the growing integration of technology into senior healthcare. Telemedicine, wearable health monitoring devices, and artificial intelligence (AI) are playing an increasingly prominent role in improving the accessibility, quality, and efficiency of care for elderly patients.
Telemedicine is enhancing access to healthcare services, especially for older adults in rural or underserved areas. With telehealth visits, elderly patients can consult doctors remotely, reducing the need for physical visits and helping to manage chronic conditions more effectively. This approach is particularly beneficial in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, which demonstrated the potential of virtual care.
Wearable health devices such as fitness trackers, smartwatches, and other monitoring systems allow healthcare professionals to track the health of their elderly patients in real time. These devices can monitor everything from heart rate to blood sugar levels, giving caregivers and doctors early warning signs of potential issues.
Artificial intelligence is also making waves in geriatrics, with AI applications helping doctors diagnose and predict diseases more accurately. AI can analyze data from medical records, lab results, and wearable devices, enabling personalized care plans for elderly patients.
3. Personalized Medicine for the Elderly
Another key trend in geriatric medicine is the growing shift towards personalized healthcare. As medical technology advances, doctors are increasingly able to tailor treatments to individual patients rather than taking a one-size-fits-all approach. This trend is particularly important in geriatric care, as the elderly population presents a diverse array of health conditions, medications, and genetic factors.
Personalized medicine, which involves customizing healthcare treatments based on a patient’s unique genetic makeup, lifestyle, and preferences, will allow for more effective management of conditions like dementia, diabetes, and heart disease. For instance, in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, personalized medicine can help identify the most effective drug combinations for patients based on their genetic markers and disease progression.
Additionally, precision nutrition is gaining traction in geriatric care. Nutrition plays a crucial role in healthy aging, and personalized diet plans that cater to an individual’s specific needs can improve outcomes for elderly patients, particularly those suffering from chronic diseases.
4. Focus on Mental Health and Cognitive Decline
Mental health in geriatrics has often been overlooked, but with an aging population and increasing awareness, this is changing rapidly. Cognitive decline, including diseases like Alzheimer’s and other forms of dementia, is becoming a major focus in geriatric medicine.
Approximately 50 million people worldwide are living with dementia, and this number is expected to triple by 2050. As a result, there is an increasing need for mental health services tailored to seniors, especially in the areas of early detection and intervention.
In response, healthcare providers are prioritizing early diagnosis and cognitive therapies to manage dementia and improve quality of life for patients. Advances in neuroimaging and genetic testing are helping doctors detect signs of cognitive decline at earlier stages, potentially slowing the progression of diseases like Alzheimer’s. Additionally, cognitive rehabilitation programs that focus on enhancing memory and daily functioning are gaining popularity in geriatrics.
5. Home Healthcare and Aging in Place
Many older adults prefer to remain in their own homes as they age, a concept known as aging in place. This preference is reshaping how healthcare is delivered to seniors. Home healthcare services are on the rise, and geriatric medicine is adjusting to accommodate this shift.
Home healthcare allows elderly patients to receive care for chronic conditions, physical therapy, and even end-of-life care in the comfort of their homes. Home health aides, physical therapists, and doctors can visit seniors in their homes, reducing hospital admissions and improving overall satisfaction.
Additionally, smart homes equipped with sensors, fall detection systems, and voice-activated assistants are increasingly popular. These technologies enable elderly individuals to live more independently and ensure that help is available when needed, enhancing both safety and quality of life.
6. Geriatric Workforce Development
As the demand for geriatric care increases, there is a growing need for healthcare professionals with specialized expertise in the needs of older adults. Geriatric nursing, in particular, is one of the fastest-growing specialties, and universities and medical schools are responding by expanding training programs in geriatric care.
Healthcare systems are also creating more collaborative models where geriatrics specialists, nurses, social workers, and psychologists work together to address the multifaceted needs of aging populations. As the baby boomer generation continues to age, the shortage of geriatric professionals will need to be addressed through better training, recruitment, and retention strategies.
Conclusion
The future of geriatric medicine is both promising and challenging, as it strives to meet the growing needs of an aging population. The integration of technology, personalized medicine, and mental health services, combined with an increased focus on aging in place and home healthcare, are transforming how healthcare is delivered to older adults. By 2025, these trends will not only reshape geriatric care but also improve the quality of life for millions of elderly individuals worldwide. As we continue to advance in these areas, the future of geriatric medicine will be more holistic, patient-centered, and accessible than ever before.