Immunotherapy in GVHD Treatment A New Hope for Patients
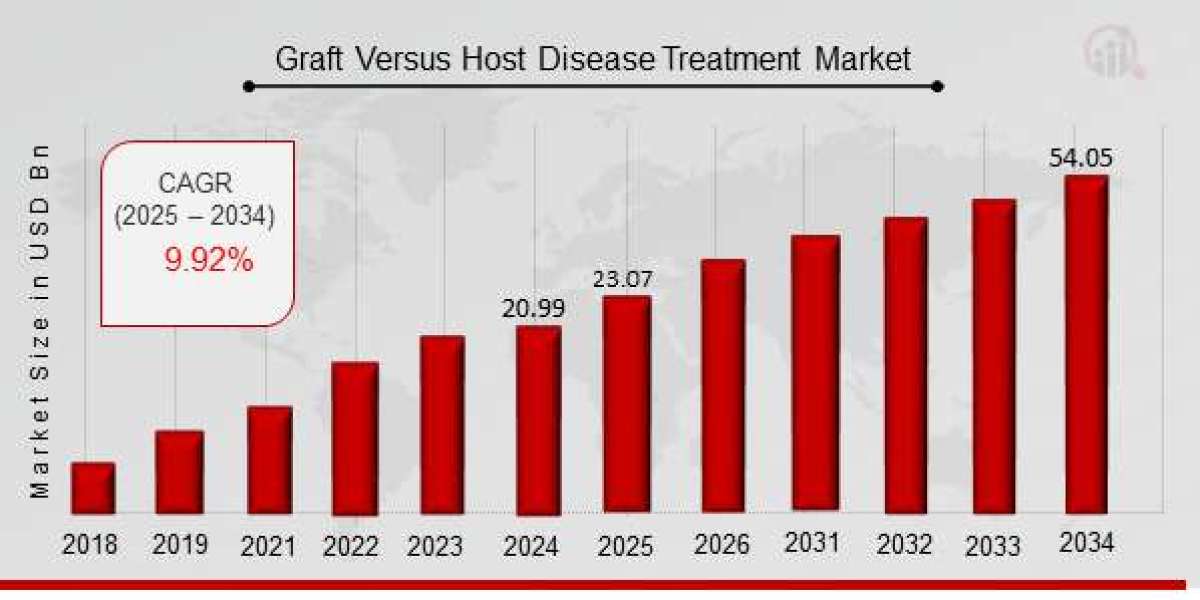
Graft Versus Host Disease (GVHD) is a severe complication that arises after a stem cell or bone marrow transplant, where the donor’s immune cells attack the recipient’s body. This life-threatening condition remains a major challenge in the realm of hematologic transplants and can significantly impact patients' quality of life. However, recent advances in immunotherapy have provided a new avenue for treatment, offering hope to many individuals who would otherwise face limited options.
Immunotherapy, which harnesses the body’s immune system to treat diseases, has emerged as a promising treatment option for GVHD in recent years. This approach is transforming the way GVHD is managed, offering more targeted, effective, and less toxic therapies compared to traditional treatments like steroids and immunosuppressive drugs. In this blog, we will explore how immunotherapy is reshaping GVHD treatment, its current applications, and its future potential.
The Role of Immunotherapy in GVHD Treatment
Immunotherapy works by either stimulating the immune system to fight cancer or modulating it to reduce harmful inflammation, as is necessary in the case of GVHD. GVHD occurs when the donor’s immune cells, which are transplanted along with stem cells, recognize the recipient's body as foreign and begin attacking it. The immune system’s reaction can lead to inflammation and damage in organs such as the skin, liver, and gastrointestinal tract. Traditional treatments, such as steroids, aim to suppress the immune response, but they come with a range of side effects, including weakened immunity, increased risk of infections, and other long-term complications.
Immunotherapy provides a more specific approach, targeting only the cells that are responsible for the harmful immune response in GVHD. By reprogramming the immune system or introducing new agents that can block harmful immune activity, immunotherapy offers a more controlled way to treat GVHD. One of the most promising forms of immunotherapy is immune checkpoint inhibitors, which work by blocking certain proteins that prevent immune cells from attacking cancer or infected cells. These inhibitors have already shown promise in cancer treatments, and their application in GVHD is becoming increasingly important.
Current Applications of Immunotherapy in GVHD Treatment
Several immunotherapeutic approaches are currently being explored and used to treat GVHD, with some already making an impact in clinical practice.
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
Immune checkpoint inhibitors, such as nivolumab and pembrolizumab, are gaining attention for their role in treating GVHD. These inhibitors work by blocking the checkpoints in the immune system that usually prevent immune cells from attacking healthy cells. When these checkpoints are blocked, immune cells become more active and can better target the underlying cause of GVHD. These drugs have shown promising results in reducing GVHD symptoms and improving survival rates in patients who do not respond well to steroids and other treatments.
Adoptive T-Cell Therapy
Adoptive T-cell therapy is another immunotherapeutic approach showing promise for GVHD treatment. This involves isolating T-cells (immune cells) from the patient or a donor, modifying them in a laboratory setting to better target the GVHD-causing cells, and then reinfusing them into the patient. The goal is to boost the body’s immune system’s ability to fight the disease while reducing the damage to healthy tissue. This treatment has shown positive results in early clinical trials, demonstrating its potential as a powerful and targeted treatment option for patients with severe GVHD.
Regulatory T-Cell Therapy
Regulatory T-cells (Tregs) play a crucial role in controlling the immune response and maintaining tolerance to the body’s own cells. In patients with GVHD, the immune system’s ability to control the graft’s immune activity is often impaired. Regulatory T-cell therapy aims to reintroduce or boost the activity of Tregs to restore immune tolerance and reduce the harmful effects of GVHD. Early studies have shown that Treg therapy can help mitigate GVHD symptoms without compromising the body’s defense mechanisms against infections.
Monoclonal Antibodies
Monoclonal antibodies are laboratory-made molecules that can mimic the immune system’s ability to fight off harmful pathogens. In GVHD treatment, monoclonal antibodies are being used to target specific immune system components that drive the disease, such as interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α). By neutralizing these key molecules, monoclonal antibodies can help reduce inflammation and control GVHD symptoms. Several monoclonal antibody therapies are in clinical trials, offering the potential for a more effective and less toxic option for managing GVHD.
Benefits and Challenges of Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy’s primary benefit lies in its ability to offer more targeted treatment compared to traditional therapies. By focusing on specific immune pathways involved in GVHD, immunotherapy can effectively manage the condition without causing the extensive side effects typically associated with immunosuppressive drugs. This results in a better quality of life for patients and fewer long-term complications.
However, like all treatments, immunotherapy has its challenges. One of the primary hurdles is that immunotherapy can sometimes lead to overactive immune responses, which can worsen GVHD or lead to other autoimmune-related complications. This requires careful monitoring and management by healthcare providers. Additionally, immunotherapy is often expensive, which may limit access for some patients. Further research and clinical trials are necessary to refine these therapies and make them more widely accessible.
The Future of Immunotherapy in GVHD Treatment
Looking ahead, the future of immunotherapy in GVHD treatment looks promising. Researchers are continuing to explore new therapeutic agents, combinations, and ways to enhance the effectiveness of existing treatments. Personalized immunotherapy, where treatments are tailored to the individual’s immune profile, is expected to be a key area of development. By customizing therapies based on a patient’s genetic makeup and immune response, doctors can improve outcomes and minimize the risk of side effects.
Furthermore, the integration of biomarkers into immunotherapy treatment plans will help clinicians better predict which patients will respond well to certain therapies, optimizing the chances of successful treatment. As more treatments are developed and clinical trials expand, immunotherapy may become a standard part of GVHD management, offering patients better outcomes and fewer complications.
Conclusion
Immunotherapy is revolutionizing the treatment landscape for Graft Versus Host Disease, providing patients with new hope for better outcomes. From immune checkpoint inhibitors to adoptive T-cell therapy, these advanced treatments are offering more precise, targeted ways to manage and even prevent GVHD. While challenges remain, the future of immunotherapy in GVHD treatment is bright, and continued advancements in this field promise to improve patient care and quality of life. For patients battling GVHD, the potential of immunotherapy represents a significant step forward in the fight against this debilitating condition.